The Rise of Alternative Proteins: Plant-Based and Lab-Grown Foods Shape Industry
As we become more conscious of the environmental impact of our food choices, the demand for alternative proteins is on the rise. Plant-based and lab-grown proteins are shaping the food industry, and their popularity is only increasing.
Plant-based proteins are derived from sources such as soy, peas, and chickpeas, and can be used to create meat substitutes that look, taste, and even bleed like real meat. On the other hand, lab-grown proteins are produced by cultivating animal cells in a lab, and can be used to create meat without the need for animal slaughter. The technology behind lab-grown proteins is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize the food industry and reduce the environmental impact of animal agriculture.
The rise of alternative proteins is not just driven by environmental concerns, but also by health and ethical considerations. Plant-based proteins are often lower in saturated fat and higher in fiber than animal-based proteins, which can lead to improved health outcomes. Additionally, many people choose to avoid animal products for ethical reasons, such as concerns about animal welfare and the treatment of farm workers.
The Growing Demand for Alternative Proteins
As we move towards a more sustainable and health-conscious future, the demand for alternative proteins is on the rise. In recent years, we have seen a significant shift in consumer preferences towards plant-based and lab-grown foods. This trend is driven by a number of factors, including environmental and health concerns, as well as changing consumer preferences and trends.
Environmental and Health Concerns
One of the primary drivers of the growing demand for alternative proteins is environmental concerns. The production of traditional animal-based proteins is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. In contrast, alternative proteins have a much lower environmental impact, making them a more sustainable choice.
Additionally, alternative proteins are often considered to be healthier than traditional animal-based proteins. Plant-based proteins, for example, are typically lower in saturated fat and higher in fiber, making them a healthier choice for many consumers. Lab-grown proteins, on the other hand, can be produced without the use of antibiotics or hormones, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses and other health concerns.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Another key driver of the growing demand for alternative proteins is changing consumer preferences and trends. In recent years, we have seen a significant shift towards plant-based and vegetarian diets, driven by concerns over animal welfare, health, and the environment. As a result, many consumers are actively seeking out alternative protein sources.
At the same time, we are also seeing a rise in the popularity of lab-grown proteins. While still a relatively new technology, lab-grown proteins offer a number of benefits over traditional animal-based proteins, including a lower environmental impact, a reduced risk of foodborne illnesses, and the ability to produce proteins that are identical to those found in traditional animal-based products.
Overall, the growing demand for alternative proteins is a reflection of changing consumer preferences and a growing awareness of the environmental and health impacts of traditional animal-based proteins. As we continue to move towards a more sustainable and health-conscious future, it is likely that the demand for alternative proteins will only continue to grow.
Plant-Based Proteins: The Future of Food?
Types of Plant-Based Proteins
We are seeing a significant rise in the popularity of plant-based proteins as an alternative to traditional animal-based proteins. There are various types of plant-based proteins available in the market, including soy, pea, rice, hemp, and many others. Soy protein, which is derived from soybeans, is one of the most popular plant-based proteins and is widely used in various food products. Pea protein, which is derived from yellow peas, is also gaining popularity due to its high protein content and easy digestibility.
Nutritional Value and Benefits
Plant-based proteins have several nutritional benefits. They are typically low in saturated fats, high in fiber, and contain various essential vitamins and minerals. Additionally, plant-based proteins are environmentally sustainable, as they require fewer resources to produce compared to animal-based proteins. Studies have shown that a diet rich in plant-based proteins can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Challenges and Limitations
While plant-based proteins have many benefits, there are also some challenges and limitations. One of the main challenges is the taste and texture of plant-based proteins, which can be different from traditional animal-based proteins. Additionally, some plant-based proteins may not contain all the essential amino acids needed for optimal health. However, with advancements in technology and innovation, we are seeing significant improvements in the taste and texture of plant-based proteins, as well as the development of complete plant-based protein sources.
In conclusion, plant-based proteins are a promising alternative to traditional animal-based proteins. They offer several nutritional benefits and are environmentally sustainable. While there are some challenges and limitations, we are seeing significant advancements in the development of plant-based proteins, and we believe that they will continue to play a significant role in shaping the future of the food industry.
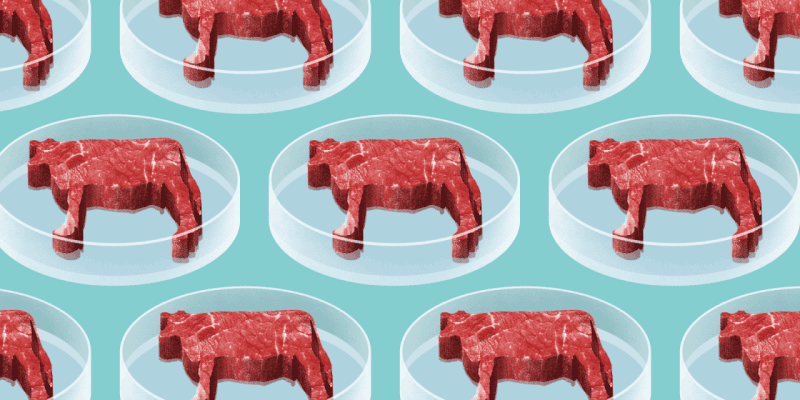
Lab-Grown Proteins: The Next Frontier?
What are Lab-Grown Proteins?
Lab-grown proteins, also known as cultured or cell-based proteins, are created by using animal cells to grow meat, dairy, and other animal products in a lab. These cells are extracted from animals and then grown in a controlled environment using a nutrient-rich solution. The resulting product is identical to conventionally produced animal products, but without the need for animal slaughter.
Advantages and Disadvantages
One of the main advantages of lab-grown proteins is their potential to reduce the environmental impact of animal agriculture. According to a report by the Good Food Institute, cultured meat could reduce land use by 90%, greenhouse gas emissions by 74-87%, and water use by 82-96% compared to conventional meat production. Additionally, lab-grown proteins could address concerns around animal welfare and food safety.
However, there are also some potential disadvantages to consider. The production of lab-grown proteins requires a significant amount of energy and resources, which could result in a high carbon footprint. Additionally, the cost of production is currently much higher than conventional animal products, which could limit their accessibility to consumers.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
The development of lab-grown proteins raises several regulatory and ethical considerations. In the United States, the FDA and USDA are currently working to establish a regulatory framework for the production and labeling of these products. Additionally, there are concerns around the use of fetal bovine serum, a nutrient-rich solution used in the production of some lab-grown proteins, which is derived from the blood of unborn calves.
From an ethical standpoint, some argue that the production of lab-grown proteins is still reliant on animal cells and therefore does not address the ethical concerns around animal exploitation. Others argue that it could be a step towards reducing animal suffering and promoting a more sustainable food system.
Overall, the development of lab-grown proteins has the potential to revolutionize the food industry and address some of the environmental and ethical concerns associated with animal agriculture. However, there are still several challenges to overcome before these products become widely available and accessible to consumers.
The Impact on the Food Industry
Alternative proteins are rapidly transforming the food industry. As we continue to see a shift towards more sustainable and ethical food choices, plant-based and lab-grown foods are becoming increasingly popular. This shift is not only driven by consumer demand but also by the need for more environmentally friendly and efficient food production methods. In this section, we will explore the impact of alternative proteins on the food industry.
Market Trends and Growth Opportunities
The market for alternative proteins is rapidly expanding. According to a report by Roland Berger, the alternative protein ingredients market size is estimated at around USD 14 billion, with annual growth rates varying between 5-50% over the coming years. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for plant-based and lab-grown foods, as well as the need for more sustainable and efficient food production methods.
As the market for alternative proteins continues to grow, there are numerous growth opportunities for companies in the food industry. For example, companies can invest in research and development to create new and innovative plant-based and lab-grown food products. They can also partner with alternative protein start-ups or invest in them to gain a foothold in the market.
Challenges and Obstacles
Despite the growth opportunities, there are also challenges and obstacles that companies in the food industry must overcome. One of the main challenges is the cost of producing alternative proteins. Currently, plant-based and lab-grown foods are more expensive to produce than traditional animal-based products. This cost is due to the high cost of research and development, as well as the cost of scaling up production.
Another challenge is consumer acceptance. While there is a growing demand for alternative proteins, some consumers are still hesitant to try plant-based or lab-grown foods. This hesitation is often due to a lack of understanding about the nutritional value and taste of these products.
The Future of Food
The rise of alternative proteins is shaping the future of food. As we continue to see a shift towards more sustainable and ethical food choices, plant-based and lab-grown foods will become increasingly popular. In the future, we can expect to see more innovative plant-based and lab-grown food products that are more affordable and accessible to consumers.
The food industry will also need to adapt to this shift towards alternative proteins. Companies that are able to innovate and offer more sustainable and ethical food choices will be better positioned to succeed in the market. Overall, the future of food looks bright as we continue to see a shift towards more sustainable and ethical food choices.