Food Safety 101: Your Ultimate Guide to Safe and Healthy Eating
When it comes to food safety, knowledge is key. We all want to eat delicious and nutritious food, but we also want to make sure that it’s safe to eat. That’s why I’ve put together a comprehensive guide to food safety that covers everything you need to know to keep yourself and your loved ones healthy.
Food safety is an important issue that affects everyone. Whether you’re a professional chef or a home cook, it’s essential to understand the basics of food safety to prevent foodborne illnesses. This guide covers topics such as proper food handling and preparation, safe cooking temperatures, and how to store and reheat leftovers. I also provide tips on how to avoid cross-contamination and how to keep your kitchen clean and sanitary.
The Importance of Food Safety
As a society, we rely on a safe and secure food supply. Food safety is an essential aspect of public health and a critical part of maintaining a healthy population. It is essential to understand the importance of food safety to ensure that we prevent foodborne illnesses, which can have severe consequences on our health.
What is Food Safety?
Food safety is the practice of ensuring that food is free from harmful contaminants and pathogens that could cause illness or injury. It involves preventing contamination of food at all stages of the food supply chain, from production to consumption.
Why is Food Safety Important?
Food safety is crucial because contaminated food can cause severe illness and even death. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 600 million people worldwide suffer from foodborne illnesses every year, and 420,000 people die as a result.
Foodborne illnesses can be caused by a variety of contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, parasites, and chemicals. Contaminated food can cause symptoms ranging from mild stomach upset to severe illness, including kidney failure, paralysis, and death.
Food safety is also essential for maintaining public confidence in the food supply. When consumers trust that their food is safe, they are more likely to consume it, which has significant economic benefits.

The Science Behind Food Safety
Food safety is based on the principles of microbiology, toxicology, and epidemiology. Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites, that can cause foodborne illnesses. Toxicology is the study of poisons and their effects on the body, while epidemiology is the study of the patterns and causes of disease in populations.
By understanding the science behind food safety, we can develop effective strategies for preventing foodborne illnesses. These strategies include implementing food safety regulations, educating food handlers and consumers, and monitoring the food supply for potential contaminants.
Overall, food safety is essential for protecting public health and maintaining a safe and secure food supply. By understanding the importance of food safety and the science behind it, we can work together to prevent foodborne illnesses and ensure that everyone has access to safe and healthy food.
Basic Food Safety Practices
When it comes to food safety, it’s important to follow basic practices to ensure that we are keeping ourselves and others safe from foodborne illnesses. These practices include cleaning, separating, cooking, and chilling.
Clean
Before handling any food, we should always wash our hands with soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds. We should also make sure to clean all surfaces, utensils, and cutting boards that will come into contact with food. This helps prevent the spread of harmful bacteria that can cause illness.
Separate
When preparing food, it’s important to keep raw meat, poultry, and seafood separate from other foods like vegetables and fruits. This helps prevent cross-contamination, which can lead to foodborne illness. We should use separate cutting boards and plates for raw and cooked foods to avoid contamination.
Cook
Cooking food to the proper internal temperature is essential for killing harmful bacteria. We should use a food thermometer to ensure that meat, poultry, and seafood reach their safe internal temperatures. It’s also important to cook eggs until the yolks and whites are firm.
Chill
Properly storing food in the refrigerator or freezer is important for preventing the growth of harmful bacteria. We should refrigerate perishable foods like meat, poultry, and seafood within two hours of cooking or purchasing. Leftovers should be refrigerated promptly as well.
By following these basic food safety practices, we can help prevent the spread of harmful bacteria and keep ourselves and others safe from foodborne illness.
Cooking Meat and Poultry
When it comes to cooking meat and poultry, it is important to ensure that it is cooked to a safe minimum internal temperature to kill harmful bacteria that can cause foodborne illnesses. I recommend using a food thermometer to check the temperature of the meat and poultry to ensure it has reached a safe temperature.
Beef, Veal, Lamb, Pork and Fish
For beef, veal, lamb and pork I recommend cooking it to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C) for medium-rare, 160°F (71°C) for medium, and 170°F (77°C) for well-done. Ground variations of these meats should be cooked to an internal temperature of 160°F.
Fish should be cooked to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C) or until the flesh is opaque and separates easily with a fork.
Remember to always use a food thermometer to ensure that your meat and poultry have reached a safe minimum internal temperature. It is also important to let your meat and poultry rest for a few minutes before slicing or serving to allow the juices to redistribute.
Reheating and Microwaving Food
Reheating food is a common practice, but it is important to do it safely to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria. When reheating food, we must make sure that it reaches an internal temperature of at least 165°F (74°C) to kill any bacteria that may have grown on it.
There are several methods we can use to safely reheat food:
- On stove top: Place food in a pan and heat thoroughly. Stir the food occasionally to ensure even heating.
- In oven: Place food in an oven set no lower than 325°F (160°C). Cover the food to prevent it from drying out.
- In microwave: Cover the food with a microwave-safe lid or plastic wrap to hold in moisture and provide safe, even heating. After reheating, let the food stand for a few minutes to allow the heat to distribute evenly.
It is important to note that not all food can be safely reheated. Some foods, such as cooked rice and pasta, can grow harmful bacteria when reheated. It is recommended to eat these foods cold or to reheat them to at least 165°F and eat them immediately.
When using a microwave to reheat food, we must be careful to ensure that it is heated evenly. Microwaves can create hot spots in food where bacteria can survive. To ensure even heating, we can use a turntable or rotate the food halfway through the reheating process.
To ensure that our appliances are heating food to a safe temperature, we can use an appliance thermometer to check the temperature of our oven or microwave. This can help us identify any hot or cold spots in our appliances and adjust our cooking or reheating methods accordingly.
Leftovers can be safely stored in the refrigerator for up to four days or in the freezer for up to four months. When reheating frozen food, we must thaw it first in the refrigerator or microwave before reheating it to ensure even heating.
Handling Dairy and Eggs
When it comes to dairy and eggs, there are a few things we need to keep in mind to ensure food safety. Dairy products should always be kept cold, at or below 40°F (4°C), and we should never consume dairy products that have been left out at room temperature for more than two hours. This includes milk, cheese, and yogurt.
Eggs are another food that requires careful handling to prevent foodborne illness. We should always purchase eggs from a reputable source and check the sell-by date before buying. When storing eggs, we should keep them in their original carton in the refrigerator at or below 40°F (4°C). It’s important to note that eggs should never be stored in the refrigerator door, as the temperature fluctuates too much in that area.
When it comes to cooking eggs, we should always make sure they are cooked thoroughly. This means that both the white and the yolk are firm. If we are making dishes like quiches or casseroles that contain eggs, we should make sure the internal temperature of the dish reaches at least 160°F (71°C) to kill any potential bacteria.
It’s also important to remember that we should use separate utensils and cutting boards for dairy and eggs to prevent cross-contamination. If we use a knife to cut cheese, for example, we should wash it thoroughly before using it to cut something else. The same goes for cutting boards.
Finally, we should always wash our hands thoroughly with warm, soapy water before and after handling dairy and eggs. This will help prevent the spread of bacteria and keep our food safe to eat.
Food Handlers and Hygiene
Food handlers play an important role in ensuring the safety of the food we serve. It is crucial that handlers adhere to strict hygiene practices to prevent foodborne illnesses. In this section, I will discuss two important aspects of food handler hygiene: hand hygiene and food handler training.
Hand Hygiene
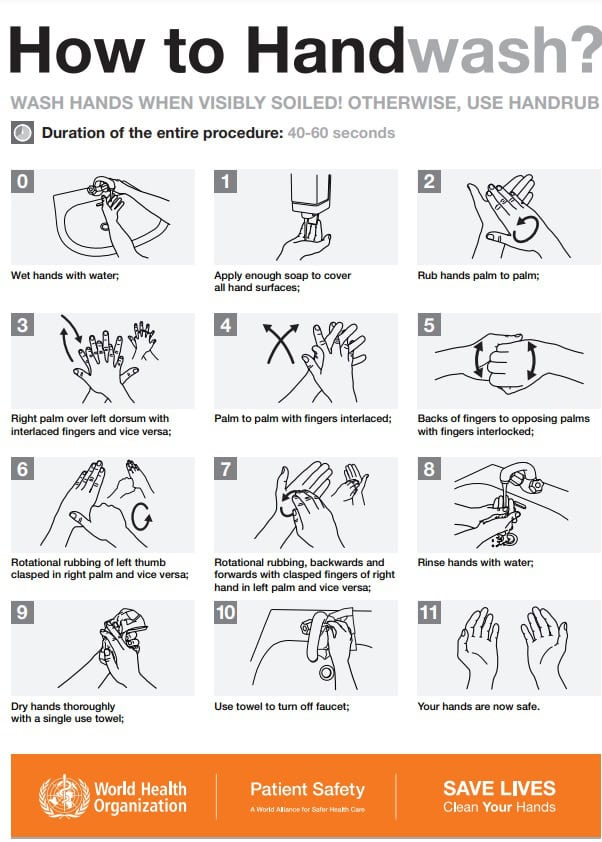
One of the most important practices for food handlers is proper hand hygiene. We must wash our hands regularly and thoroughly with soap and water. This is especially important after using the restroom, handling raw meat, and touching our face, hair, or clothing. We must also wash our hands before handling food and after handling money, taking out the trash, or doing any other task that could contaminate our hands.
When washing our hands, we should use warm water and lather our hands with soap for at least 20 seconds. We should scrub our hands, fingers, and nails, and then rinse thoroughly with running water. Finally, we should dry our hands with a clean towel or air dryer.
Food Handler Training
Food handler training is another important aspect of food safety. We must be knowledgeable about safe food handling practices, including proper cooking temperatures, storage, and cross-contamination prevention. Many states and local health departments require food handler training and certification for all food handlers.
Training programs are available online and in-person, and cover topics such as personal hygiene, foodborne illnesses, and safe food handling practices. By completing a food handler training program, we can ensure that we are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to prevent foodborne illnesses and keep our customers safe.
In conclusion, food handlers have a responsibility to maintain proper hygiene and receive adequate training to prevent foodborne illnesses. By following proper hand hygiene practices and completing food handler training, we can ensure the safety of the food they serve and protect the health of the customers.
Microbiological Hazards and HACCP
When it comes to food safety, one of the most important things to consider is the presence of microbiological hazards. These hazards can include bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can cause foodborne illness. It’s essential to have a plan in place to control these hazards, and that’s where HACCP comes in.
HACCP, or Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, is a systematic approach to identifying and controlling food safety hazards. It involves seven principles, including conducting a hazard analysis, identifying critical control points, and monitoring those points to ensure they are under control.

By implementing a HACCP plan, we can identify potential microbiological hazards in our food production processes and take steps to control them. This can include things like ensuring proper cooking temperatures, implementing sanitation procedures, and monitoring for potential contamination.
It’s important to note that not all microbiological hazards can be eliminated entirely, but we can take steps to reduce the risk of foodborne illness. As such, it’s essential to have a comprehensive HACCP plan in place to ensure the safety of our food products.
In addition to implementing a HACCP plan, it’s also essential to stay up-to-date on the latest information and guidance related to microbiological hazards and food safety. This can include monitoring for any outbreaks or recalls, staying informed on best practices for food safety, and regularly reviewing and updating HACCP plan to ensure it remains effective.
By taking a proactive approach to food safety and implementing a comprehensive HACCP plan, we can help ensure the safety and well-being of our customers and prevent the spread of foodborne illness.
Conclusion
Ensuring food safety is an ongoing process that requires the collective efforts of everyone involved in the food industry, from producers and processors to transporters, suppliers, preparers, and retailers. It also requires the participation of officials at the local, state, and federal levels, as well as consumers who select and prepare food.
As we have learned, there are several key steps to ensuring food safety. These include properly storing, cooking, and handling food, as well as being aware of potential foodborne illnesses and taking steps to prevent them. By following these guidelines, we can help reduce the risk of foodborne illness and ensure that the food we eat is safe and healthy.
It is important to note that food safety is not just a matter of personal responsibility, but also a public health issue. By taking steps to ensure food safety, we can help prevent outbreaks of foodborne illness and protect the health of our communities.
There are many resources available to help us learn more about food safety and how to ensure that the food we eat is safe. These include videos, online guides, and educational materials from government agencies and other organizations. By taking advantage of these resources, we can become more informed and better equipped to ensure the safety of our food.
Finally, it is worth noting that fresh fruits and vegetables are an important part of a healthy diet, but they can also pose a risk of foodborne illness if not handled properly. By following the same guidelines for storing, cooking, and handling fruits and vegetables as we do for other foods, we can help ensure that they are safe to eat.






