Carbon – The Basic Body Matrix Element
Our bodies are made of cells and water is the major medium without which biochemical reactions would not be possible, but when you zoom in even further into the basis of cell structure, what do you think you would find? There’s one element who rightfully holds the title of leading actor.

How come carbon atom became the lead actor in this game of life?
Carbon is the lead actor in this game of life and all vital molecules in our bodies are composed of carbon compounds. But it would be one very boring play if the only guy who appears in every scene is the same. It’s not that he’s not awesome and can not carry the whole play on his shoulder, but we can get a much more interesting plot if we also have some supporting roles to spice up the story, and in this game of life, that would be hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur.
But why carbon of all elements? First of all, carbon bonds to itself. Many elements have this feature, but carbon is most effective at it. Practically there’s no limit for him in making various chains or rings. And secondly, carbon bonds as well to those other elements, mentioned at the beginning, and forms foundational structures necessary for life creation and maintenance.
How do carbon atoms bond between each other?
Carbon has four possible places for bonding so you can easily do the math yourself – it can be:
- 4 single bonds, or
- 1 double and 2 single, or
- 1 triple and 1 single, or?
- yes, you figured it out right – 2 double bonds.
Double bonds to oxygen atoms are of particular importance in biochemicals. Also, different types of bonds have different strengths and affect physical properties of substances, such as melting, boiling points and solubility.
Carbon with other supporting elements
When carbon is at play with any of supporting roles elements he’s making particular groupings that are called functional groups. Those parts of the molecule are the places where chemical reactions between different molecules occur.
Based on those functional groups we distinct certain compounds as alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, esters, amines, to mention just a few.
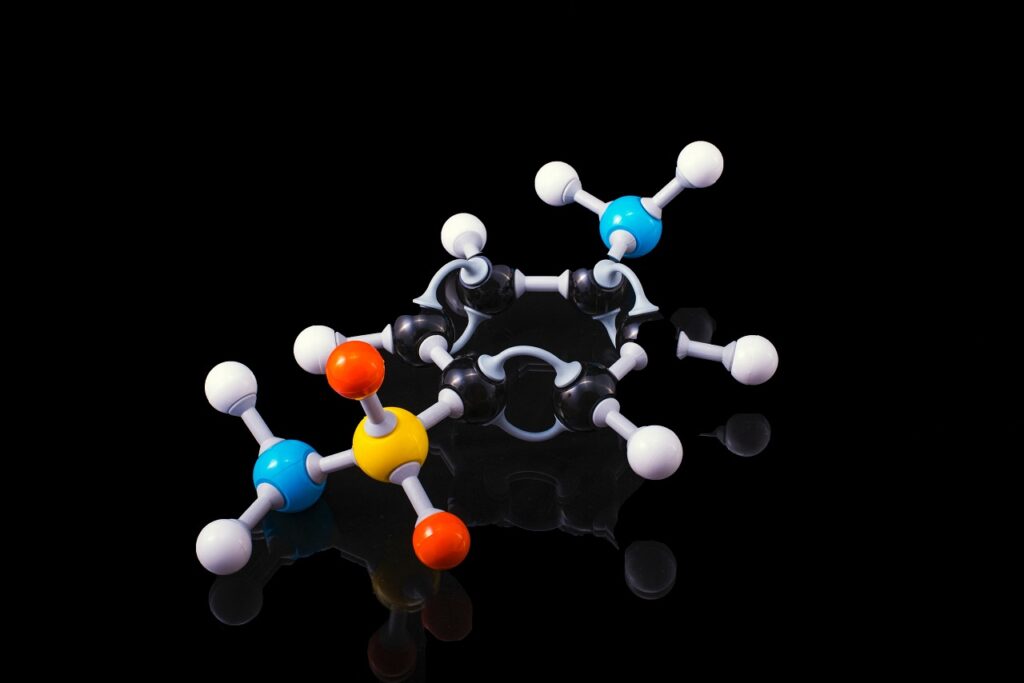
Double bonds and cis-trans isomerism
One important term of double bonding that you were surely met with in your life, if nowhere else then at least in example of controversial trans fats, is cis-trans positions of molecular structures. This property of the compound is a consequence of the structural formula of the same molecule content, but different spatial positioning which is called isomerism. Two most common types in biological systems are cis and trans isomers which means that functional groups are on the same or the opposite sides of double bond. As example we’ve already mentioned Cis isomers are the normal form of fatty acids, whereas food processing tends to convert some of the cis isomers to the trans isomers, which are strongly unwanted in today’s diets because of their linkage to cardiovascular diseases of our time.
Well, enough said, before we lose ourselves in the complexity of chemical structures, let’s get to the more visible stuff in everyday life!